
Mental Health & Fluid Retention Calculator
Assess Your Risk Factors
Answer the following questions to see how your mental health habits might be contributing to fluid retention.
Your Fluid Retention Risk Assessment
Key Mental Health Triggers of Fluid Retention
| Trigger | Effect on Fluid Retention | Associated Mental Health Impact | Badge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Stress | Elevates cortisol → sodium retention → edema | Heightened anxiety, irritability | Cortisol |
| Poor Sleep | Disrupts hormone balance, increases inflammation | Depressive mood, reduced focus | Stress |
| Unhealthy Diet | Directly adds sodium, amplifies cortisol-driven retention | Emotional eating driven by anxiety | Sodium |
| Physical Inactivity | Reduces muscle pump that pushes fluid back to circulation | Low motivation, depressive inertia | Stress |
| Medication Side-effects | Some antidepressants increase weight and water retention | Improved mood but new physical discomfort | Cortisol |
Ever felt puffier after a stressful week or noticed swelling when anxiety spikes? That isn’t just in your head-there’s a real link between fluid retention and mental health. This article unpacks how emotions, hormones, and everyday habits can trap water in your body, and what you can do to break the cycle.
Key Takeaways
- Stress hormones like cortisol can cause the body to hold onto sodium, leading to edema.
- Depression and anxiety often coincide with lifestyle changes (poor diet, inactivity) that worsen fluid buildup.
- Some antidepressants and antipsychotics have side‑effects that promote water retention.
- Simple habits-hydration, balanced salt intake, movement, and stress‑management techniques-can dramatically reduce swelling.
- Persistent or painful swelling warrants medical evaluation to rule out underlying heart, kidney, or liver issues.
What Is Fluid Retention?
Fluid Retention is the accumulation of excess water in the body’s tissues, commonly called edema. It often appears in the feet, ankles, hands, or abdomen and may cause a feeling of tightness or heaviness. The condition arises when the balance between fluid intake, blood pressure, and the lymphatic system’s ability to drain water is disrupted.
How Mental Health Enters the Picture
Mental Health refers to our emotional, psychological, and social well‑being. Conditions such as stress, anxiety, and depression don’t just affect thoughts; they trigger physiological responses that can alter fluid balance.
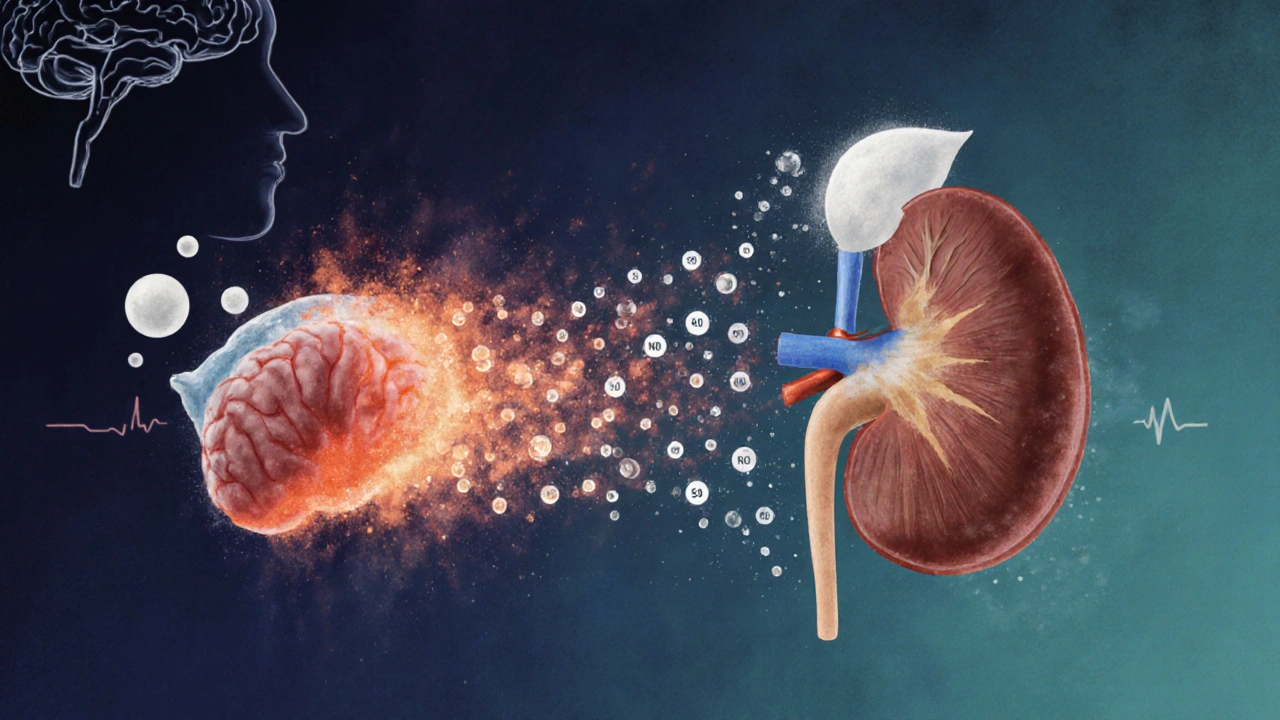
Hormonal Bridge: Cortisol and Sodium
Cortisol is the body’s primary stress hormone, released by the adrenal glands during mental strain. When cortisol spikes, it signals the kidneys to retain sodium, a key driver of water retention. This mechanism helped our ancestors survive short‑term threats, but chronic stress keeps cortisol elevated, leading to persistent puffiness.
Common Mental‑Health‑Related Triggers of Fluid Retention
| Trigger | Effect on Fluid Retention | Associated Mental Health Impact | Typical Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Stress | Elevates cortisol → sodium retention → edema | Heightened anxiety, irritability | Work deadline pressure for weeks |
| Poor Sleep | Disrupts hormone balance, increases inflammation | Depressive mood, reduced focus | Late‑night screen time, insomnia |
| Unhealthy Diet (high‑salt, processed foods) | Directly adds sodium, amplifies cortisol‑driven retention | Emotional eating driven by anxiety | Fast‑food binge after a stressful day |
| Physical Inactivity | Reduces muscle pump that pushes fluid back to circulation | Low motivation, depressive inertia | Day‑long couch‑surfing during a depressive episode |
| Medication Side‑effects | Some antidepressants increase weight and water retention | Improved mood but new physical discomfort | Starting an SSRI and noticing swollen ankles |
Medication Matters: Antidepressants and Diuretics
Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclics can cause weight gain, increased appetite, and fluid retention as side‑effects. While they are vital for treating depression, clinicians often monitor weight and swelling during the first months.
Conversely, Diuretics are medications that promote urine production, helping the body dispose of excess fluid. They’re commonly prescribed for heart failure or hypertension but can be used short‑term to manage severe edema linked to stress‑induced cortisol spikes. Always discuss dosing with a doctor; over‑use can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
Interplay With Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety often triggers rapid breathing and the “fight‑or‑flight” response, flooding the bloodstream with stress hormones. This surge encourages the kidneys to hold onto sodium, creating that tight‑ness you feel in the chest or limbs.
Depression can lead to sedentary behavior and poor dietary choices, both of which increase the risk of edema. Moreover, the hormone serotonin, which antidepressants aim to balance, also influences blood vessel tone-altering fluid distribution.
Practical Steps to Reduce Fluid Retention Linked to Mental Health
- Mindful Salt Management: Aim for less than 2,300mg of sodium per day. Swap salty snacks for fruits, nuts, and unsalted seeds. Reading nutrition labels helps keep hidden salt out of your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking 1.5‑2L of water daily encourages the kidneys to flush excess sodium. Counterintuitively, dehydration makes the body cling to every drop.
- Move Daily: Even a 15‑minute walk boosts muscle contraction, which pushes fluid back toward the heart. Gentle yoga or stretching also activates the lymphatic flow.
- Stress‑Reduction Techniques: Practice deep‑breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or short mindfulness sessions (5‑10minutes) to lower cortisol levels.
- Sleep Hygiene: Keep a consistent bedtime, limit screens an hour before sleep, and create a dark, cool sleeping environment to support hormone regulation.
- Nutrition Focus: Include potassium‑rich foods like bananas, avocado, and leafy greens to counterbalance sodium. Magnesium (found in nuts, seeds, dark chocolate) helps relax blood vessels.
- Review Medications: If you notice swelling after starting a new antidepressant, talk to your prescriber. Sometimes a dosage tweak or a different class resolves the issue.
- Professional Check‑ups: Persistent swelling in one limb, sudden weight gain, or pain should prompt a visit to a GP to rule out heart, kidney, or liver conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Occasional puffiness is often harmless, but these red flags mean you need a clinician’s eyes:
- Swelling that doesn’t improve after a few days of self‑care.
- Painful, tight skin or redness-a sign of infection or deep‑vein thrombosis.
- Rapid weight gain (more than 2kg in a week) without diet changes.
- Shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood‑tinged sputum.
- History of heart failure, kidney disease, or liver cirrhosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can everyday stress really cause noticeable swelling?
Yes. Chronic stress keeps cortisol levels high, prompting the kidneys to retain sodium. This extra salt pulls water into the tissues, especially in the lower legs and face.
Do all antidepressants cause fluid retention?
Not all, but many SSRIs, SNRIs, and tricyclics list weight gain or edema as possible side‑effects. The degree varies by individual and dosage. Discuss concerns with your psychiatrist; sometimes switching to a different class eliminates the issue.
Is drinking more water a myth for reducing edema?
No myth-adequate hydration signals the kidneys to excrete excess sodium. Skipping water makes the body cling to the fluid it already has, worsening puffiness.
Can dietary potassium actually help with edema?
Potassium balances sodium levels by encouraging the kidneys to release more salt in urine. Foods like bananas, oranges, spinach, and beans are natural helpers.
Should I take a diuretic if my swelling is stress‑related?
Only under a doctor’s guidance. Short‑term diuretics can reduce severe edema, but they don’t address the underlying stress hormone surge. Lifestyle changes and stress‑management are the sustainable solution.


Comments
Jessica Simpson
Interesting how chronic stress can crank up cortisol levels, which then makes the kidneys hold onto more sodium – basically a recipe for edema. I’ve noticed that my own stress spikes often line up with that puffy feeling in my ankles. Maybe a quick mindfulness break could be a simple buffer against that fluid lock‑up?
Ryan Smith
Oh sure, because the government’s secret agenda to keep us all slightly swollen is totally hidden in our bedtime habits. Nothing says "conspiracy" like a good night’s sleep, right?
John Carruth
When we look at the cascade of physiological events, the link between mental health and fluid balance becomes clearer than a fresh‑cut onion. Chronic stress triggers the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑adrenal axis, pushing cortisol into the bloodstream. Elevated cortisol, in turn, up‑regulates the epithelial sodium channel in the renal tubules, prompting the kidneys to retain sodium and water. The retained sodium draws water into the interstitial spaces, producing edema that is often most noticeable in the lower extremities. Poor sleep compounds this issue by disrupting the normal circadian rhythm of antidiuretic hormone, reducing the body’s ability to excrete excess water at night. Additionally, sleep deprivation increases systemic inflammation, which further enhances vascular permeability, allowing fluid to seep out of the bloodstream more readily. Dietary choices are another cornerstone; high‑salt processed foods directly supply the sodium that the body is already inclined to hold onto under stress. Emotional eating, driven by anxiety, frequently leads to over‑consumption of these very foods, creating a feedback loop that intensifies both mental distress and physical swelling. Physical inactivity removes the muscular pump that normally assists venous return, slowing the clearance of fluid from the legs and feet. Even modest daily movement, such as a brisk walk, can dramatically improve lymphatic drainage. Certain medications, particularly some antidepressants, have side‑effects that include weight gain and water retention, which can be misattributed to the underlying depressive symptoms if not carefully monitored. The good news is that each of these factors is modifiable: stress‑reduction techniques, consistent sleep schedules, low‑sodium diets, regular exercise, and close collaboration with healthcare providers to adjust medication can collectively restore fluid equilibrium. By addressing the mental health components head‑on, we are not merely treating the emotional side of illness but also preventing the cascade that leads to edema. In practice, a holistic approach that integrates psychological counseling with lifestyle coaching yields the most robust results and helps individuals reclaim both mental clarity and physical comfort.
Melodi Young
Totally spot on, you nailed it.
Tanna Dunlap
While the data is well‑presented, one cannot ignore the moral responsibility to educate the public about the dangers of self‑medicating with high‑salt comfort foods. Ignorance is not an excuse when edible choices become a silent accomplice to both mental anguish and bodily swelling.
Troy Freund
Think of the body as a river; stress is the dam, sleep is the flow, and movement is the current that keeps the water moving. When the dam is high, the river overflows its banks, just like cortisol can overflow into fluid retention.
Mauricio Banvard
Everyone’s talking about cortisol, but have you considered the hidden micro‑chips that manipulate our sleep cycles to keep us perpetually fatigued? Those little devices could be the real culprits behind the swelling epidemic.
Paul Hughes
Interesting point! 🌊 It does feel like our bodies send us subtle signals when stress builds up.
Keeping an eye on diet and movement can really help balance the tide.
Mary Latham
i think the whole stress‑edema link is overhyped, like people just love an excuse for their puffiness.
Marie Green
Feeling a little puffy can be scary, especially when you’re already stressed. Remember to be kind to yourself and maybe try a short walk or a breathing exercise.
TOM PAUL
Hey team! Let’s take this info and turn it into action – a quick stretch, a glass of water, and a deep breath can make a difference today. You’ve got this!
Ash Charles
Enough talk – start moving now! No excuses, just grab those shoes and hit the pavement. Your legs will thank you and the swelling will shrink.
Michael GOUFIER
In light of the presented evidence, it would be prudent for individuals to adopt a regimented schedule encompassing adequate nocturnal rest, a judicious reduction of sodium intake, and routine physical activity to mitigate the physiological sequelae associated with heightened cortisol concentrations.
michael Mc Laughlin
Sounds good lets try it and see how we feel later
Luke Schoknceht
The so‑called "mental health" angle is often just a convenient diversion from personal accountability. People love to blame stress for everything, from bloating to broken relationships, while ignoring the obvious lifestyle choices that lead to sodium overload. It’s a classic case of victim mentality-pretending the body is a helpless victim of cortisol spikes rather than admitting to binge‑eating chips while binge‑watching TV. Moreover, the emphasis on vague terms like "inflammation" feels like a buzzword to avoid concrete recommendations. If we stripped away the jargon, the solution would be simple: eat less salty processed food, get adequate sleep, and move your body daily. The emotional narratives about anxiety and depression are fine, but they shouldn’t become an excuse to sidestep personal responsibility. In short, the connection is real, but the narrative is inflated to fit a trendy wellness storyline.
mauricio gonzalez martinez
Actually, I think the whole calculator is a bit off‑base.