Atorvastatin: What It Is and Why It Matters
If you’ve been told you have high cholesterol, chances are your doctor mentioned atorvastatin. It’s one of the most prescribed statins because it reliably lowers LDL (the “bad”) cholesterol and helps protect your heart. In plain terms, atorvastatin tells your liver to produce less of the stuff that clogs arteries.
People take this pill for a few reasons: they have high LDL numbers, they’ve already had a heart attack or stroke, or they have risk factors like diabetes or family history of heart disease. It’s not a magic cure, but it’s an effective tool when you pair it with diet and exercise.
How Atorvastatin Works
The drug belongs to the statin class, which blocks an enzyme called HMG‑CoA reductase. Think of that enzyme as a factory line that makes cholesterol. When the line stops, your liver pulls cholesterol out of the bloodstream to make up the shortfall, dropping overall levels.
Because it targets the production step, atorvastatin works faster than lifestyle changes alone. Most people see a 30‑50% drop in LDL after a few weeks. The effect is dose‑dependent – higher doses give bigger drops but may raise the chance of side effects.
Tips for Safe Use
Start low, go slow. Your doctor will likely begin with 10 mg daily and adjust based on lab results. Don’t jump to a high dose without medical guidance.
Take it at the same time each day. Most folks prefer bedtime because the liver is most active at night, but consistency matters more than the exact hour.
Watch for muscle aches. A small percentage of users feel sore muscles or weakness. If pain is severe or lasts longer than a few days, call your doctor – they may check your blood for signs of muscle damage.
Avoid certain foods and drugs. Grapefruit juice can increase atorvastatin levels in the blood, raising side‑effect risk. Also tell your pharmacist about any other meds you’re on; some antibiotics, antifungals, and HIV drugs interact badly with statins.
Keep up with blood tests. Your doctor will check liver enzymes and cholesterol numbers after starting the pill and periodically thereafter. These checks confirm the drug is doing its job and not harming your liver.
Most side effects are mild – occasional headache, nausea, or digestive upset. Serious issues like liver problems are rare but worth monitoring.
If you miss a dose, just take it when you remember unless it’s almost time for the next one. Don’t double up; that can increase side‑effect risk.
Finally, remember that atorvastatin works best with a heart‑healthy lifestyle. Cutting back on saturated fats, adding regular walks, and quitting smoking amplify the drug’s benefits.
This tag page gathers all articles related to atorvastatin, from dosage guides to safety tips. Browse the list below for deeper dives into specific questions you might have about this cholesterol‑lowering powerhouse.
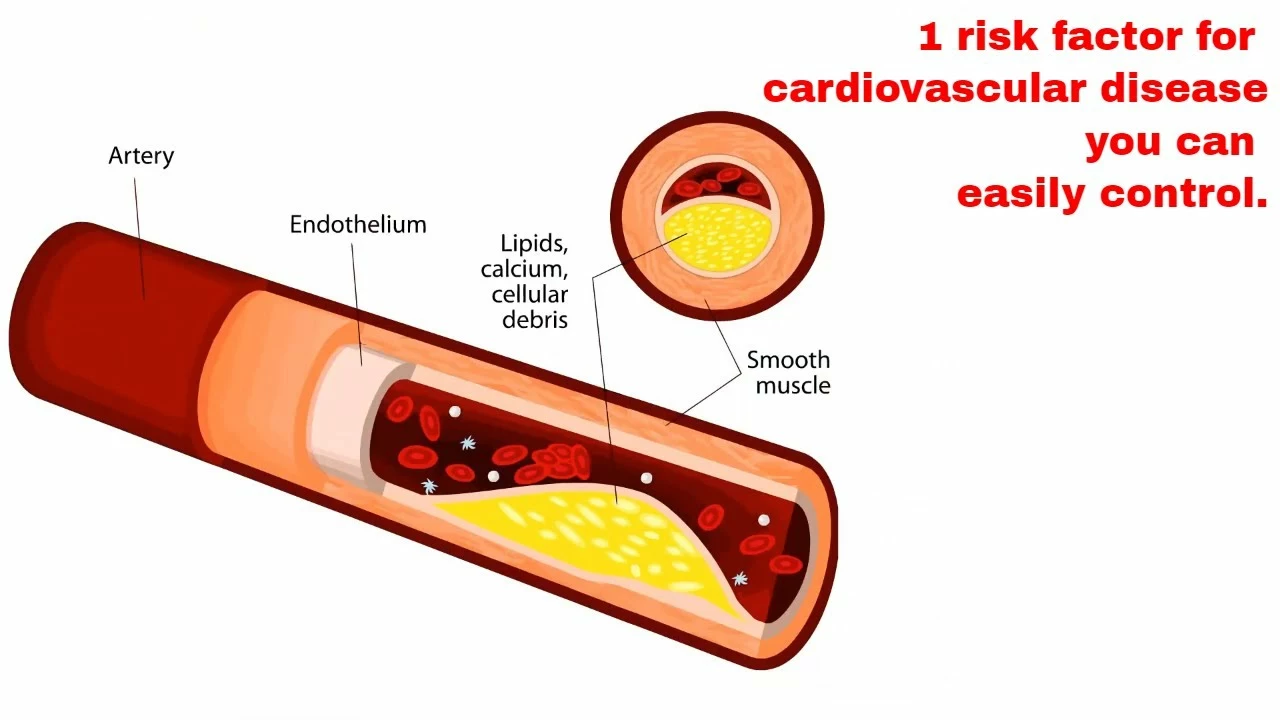
The Role of Atorvastatin in Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
As a blogger, I've been researching the role of Atorvastatin in preventing cardiovascular disease. It turns out that this medication, commonly known as a statin, plays a significant role in lowering cholesterol levels, which in turn reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes. By inhibiting an enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver, Atorvastatin helps maintain a healthy balance of good and bad cholesterol. Additionally, it's been found that this drug may also have anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to improved cardiovascular health. Overall, Atorvastatin appears to be an essential tool in our fight against cardiovascular disease.
read more