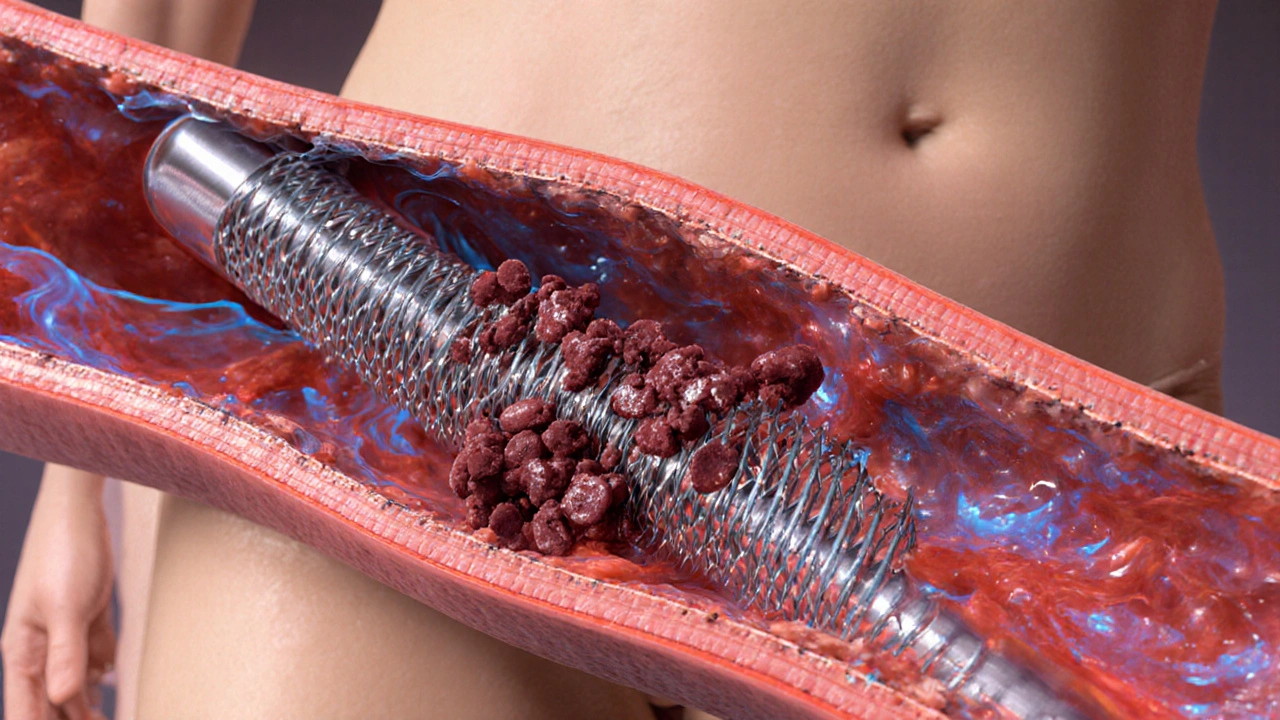
Coronary Stent
When talking about Coronary Stent, a tiny mesh tube that props open a narrowed heart artery. Also known as heart stent, it’s the core device used during a Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), a minimally invasive way to restore blood flow. The PCI process starts with angioplasty, where a balloon inflates to widen the blockage before the stent is deployed. Together, these steps keep the heart muscle fed and reduce the chance of a heart attack.
What you need to know about coronary stents
The market offers two main families of stents. A Drug‑Eluting Stent (DES) slowly releases medication that prevents the artery from narrowing again, a problem called restenosis. In contrast, a Bare‑Metal Stent (BMS) provides only structural support without the drug coating, making it a simpler, sometimes cheaper option. DESs are favored when the blockage is complex or when the patient has a higher risk of restenosis, while BMSs can be ideal for patients who may need a shorter duration of anti‑platelet therapy. Both types share the same basic attributes: they’re made of metal alloys, come in various diameters and lengths, and are crimped onto a delivery balloon catheter. Choosing the right stent depends on the artery’s size, the lesion’s length, and the patient’s overall health profile.
After the stent is placed, the real work begins with recovery and long‑term care. Patients usually stay in the hospital for a day, then start a regimen of anti‑platelet drugs like aspirin and clopidogrel to keep blood from clotting around the metal. Follow‑up appointments include checking the stented segment with a stress test or a repeat angiogram if symptoms reappear. Lifestyle changes—quitting smoking, eating heart‑healthy foods, and staying active—greatly improve the odds that the stented artery stays open. If you’re curious about the latest stent technologies or want step‑by‑step guidance on what to expect after PCI, the articles below break down everything from medication schedules to warning signs that need immediate medical attention. Let’s explore the practical tips and deeper insights you’ll find in the collection ahead.
How Obesity Increases Blood Clot Risk in Vascular Stents
Explore how obesity raises the risk of blood clot formation in vascular stents, the science behind it, and practical steps to prevent and manage thrombosis.
read more